Going up. Monday showed what the market thinks of Morrison
- Written by Mark Humphery-Jenner, Associate Professor of Finance, UNSW
The coalition’s shock victory pushed up the S&P ASX 200 1.7% in the biggest surge since Kevin Rudd was elected prime minister in 2007.
The ASX 200 measures the price of Australia’s 200 biggest public companies. The jump pushed up the value of shares across the entire market by A$33 billion. The price of one of the banks jumped 9%.
All of the polls leading up to the election had Labor ahead, with Labor apparently widening its lead[1] in the final few days.
Punters placing bets also overwhelmingly favoured Labor. Sportsbet was so confident of a Labor victory, it paid out bets on Labor early[2].
Which means the market jumped in surprise first thing on Monday.
It had been expecting a Shorten victory, and had to suddenly reprice after discovering it had been a Morrison victory.
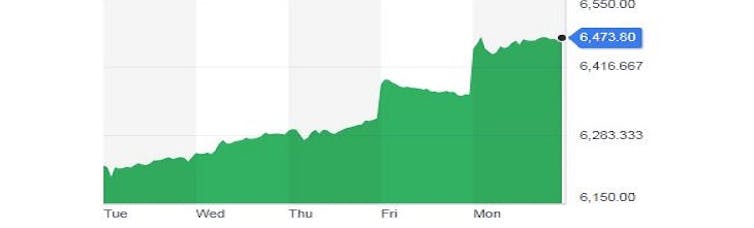 ASX 200, May 14 to May 20.
Yahoo Finance[3]
ASX 200, May 14 to May 20.
Yahoo Finance[3]
It didn’t jump for other reasons
It’s pretty clear that the jump didn’t reflect anything else, for two reasons:
it is surprises that move markets, because everything else is priced in, and the coalition victory was just about the only surprise over the weekend
we are able to compare the ASX movements with those on other markets ahead of it opening. The ASX normally follows other markets unless there is a clear local reason to do otherwise. In this case, the related market indexes in the United States, Britain and Canada had all fallen in their most recent sessions before the ASX opened. By contrast, the ASX indexes jumped sharply, suggesting a very strong positive reaction to only big piece of local news around on the day
Others down, Australia up
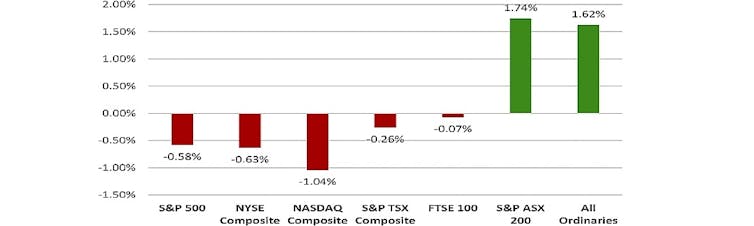 Returns on Friday May 17 in the US, Canada and UK, on May 20 in Australia.
Red = foreign indexes. Green = Australian indexes[4]
Returns on Friday May 17 in the US, Canada and UK, on May 20 in Australia.
Red = foreign indexes. Green = Australian indexes[4]
Why such a strong reaction?
It’s hard to be sure, and different government policies affect different industries differently. But there are common threads:
Property effects: Labor’s capital gains tax and negative gearing tax policies might have hurt property prices[5].
The prospect of prices somewhat stronger than they might have been might help arrest the decline in construction which might help generate employment, which might boost economic growth. Stronger prices bolster consumer confidence and support spending. They can also support it directly as people tap into equity from their homes.
Tax factors: The market generally reacts well to tax cuts. This was the case in the US[6] as Trump’s tax cuts became increasingly likely. This is due in part to the expectation that they would boost the economy. The market generally dislikes tax increases. While it is not clear whether the Coalition’s promised longer-term tax cuts[7] will materialise, they have plans for them that Labor didn’t.
Labor’s dividend imputation policy would have harmed retirees’ incomes. With it off the table they can spend and hold shares had they had before.
Banking and finance: The coalition is generally seen as more concilliatory towards the banking sector, being reticent to impose major penalties following the royal commission, and disinclined to commence it to begin with. The share price of big four banks increased significantly: from 6.27% for the Commonwealth through to 9.21% for Westpac.
Mining and energy: Labor was perceived as hostile to mining and resource companies. Several recorded strong price gains. Its seeming reluctance to acknowledge the costs of its climate change policies[8] can’t have helped.
We can’t know for sure
Other factors might include the Coalition’s approach to infrastructure and to unions, which are generally business friendly.
Often markets react to what they think markets will do, rather than to anything real. But it’s fair to say that, to start with, they are feeling better.
References
- ^ apparently widening its lead (www.theaustralian.com.au)
- ^ paid out bets on Labor early (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ Yahoo Finance (au.finance.yahoo.com)
- ^ Red = foreign indexes. Green = Australian indexes (www.asx.com.au)
- ^ might have hurt property prices (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ the case in the US (www.businessinsider.com.au)
- ^ promised longer-term tax cuts (www.liberal.org.au)
- ^ reluctance to acknowledge the costs of its climate change policies (www.theaustralian.com.au)
Authors: Mark Humphery-Jenner, Associate Professor of Finance, UNSW
Read more http://theconversation.com/going-up-monday-showed-what-the-market-thinks-of-morrison-117396







