Breakthrough in 0.05 Tesla MRI reported by HKU Engineering team in Science Journal
HONG KONG SAR - Media OutReach Newswire - 25 June 2024 - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has revolutionised healthcare with its non-ionising, non-invasive, multi-contrast and quantitative capabilities. It also presents a promising platform for future artificial intelligence-driven medical diagnoses.
However, limited accessibility, especially in low and middle-income countries, is a challenge due to high costs and specialised settings required for standard superconducting MRI scanners. These scanners are mostly found in specialised radiology departments and large imaging centres, restricting their availability in other medical settings. The need for radiofrequency shielded rooms and high-power consumption further adds to the cost and mobility limitations. Furthermore, most MRI scanners are concentrated in high-income countries at present time, presenting an exemplary case of ever-expanding global healthcare disparity.
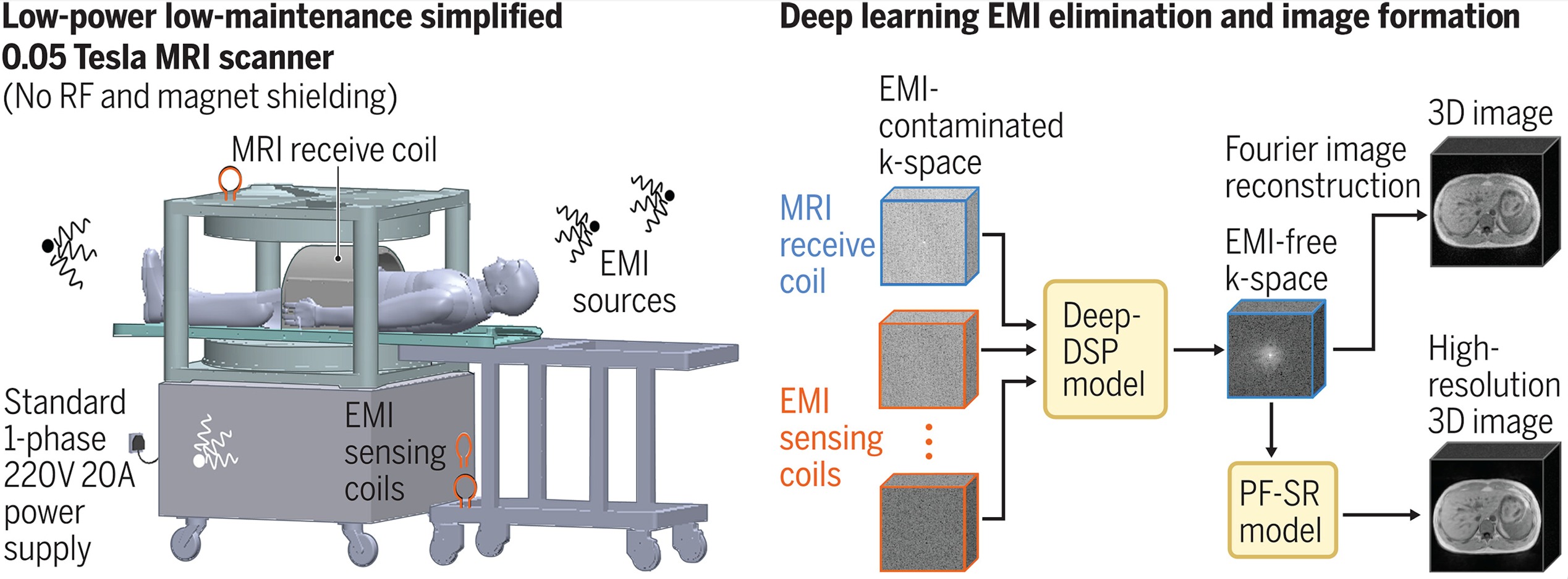
Led by Professor Ed X. Wu, Lam Woo and Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering, a research team from Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) has developed a whole-body MRI scanner that operates on a standard wall power outlet without radiofrequency or magnetic shielding cages. The machine costs only a fraction of current clinical scanners, is safer, and needs no costly infrastructure to run.
The detailed findings have been published in renowned scientific journal Science, and companied by a Science Perspective article.
The scanner developed by the HKU team uses a compact 0.05 Tesla permanent magnet and incorporates active sensing and deep learning to address electromagnetic interference (EMI) signals. Human imaging at such a low magnetic field strength has been widely viewed as challenging, if not impossible. In order to eliminate EMI signals, the researchers deployed EMI sensing coils positioned around the scanner and implemented a deep learning method to directly predict EMI-free nuclear magnetic resonance signals from acquired data. To enhance image quality and reduce scan time, the team also developed a deep learning image formation method. It integrates image reconstruction and three-dimensional multi-scale super-resolution, and leverages the homogeneous human anatomy and image contrasts available in high-field high-resolution MRI data.
The team has succeeded in implementing commonly used clinical protocols with an ultra-low-field strength of 0.05 Tesla, including T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and diffusion-weighted imaging, and optimising their contrasts for different anatomical structures. Each protocol was designed to have a scan time of 8 minutes or less, with an image resolution of approximately 2x2x8 mm³. The scanner power consumption during scanning was under 1800W, and around 300W when idle.
The HKU team conducted imaging on healthy volunteers, capturing brain, spine, abdomen, lung, musculoskeletal, and cardiac images. Deep learning signal prediction effectively eliminated EMI signals, enabling clear imaging without shielding. The brain images showed various brain tissues, while the spine images revealed intervertebral disks, spinal cord, and cerebrospinal fluid. Abdominal images displayed major structures like the liver, kidneys, and spleen. Lung images showed pulmonary vessels and parenchyma. Knee images identified knee structures such as cartilage and meniscus. Cardiac cine images depicted the left ventricle contraction, while neck angiography revealed carotid arteries.
Additionally, a new deep learning image formation approach greatly improved the 0.05 Tesla image quality for various anatomical structures, including the brain, spine, abdomen, and knee. It effectively suppressed noise and artefacts and increased image spatial resolution.
The low-power and simplified whole-body 0.05 Tesla MRI scanner developed by Professor Wu's research team is able to operate without the need for radiofrequency or magnetic shielding to address MRI accessibility. The researchers experimentally demonstrated the general utility of this scanner for imaging various human anatomical structures at whole-body level, even in the presence of strong EMI signals, with acceptable scan time. They also demonstrated the potential of deep learning image formation to substantially augment 0.05 Tesla image quality by exploiting computing and extensive high-field MRI data.
The breakthroughs reported in this study shall catalyse the development of an entirely new class of affordable, patient-centric, and deep learning-powered ultra-low-field MRI scanners, addressing unmet clinical needs in diverse healthcare settings worldwide.
"We are looking forward to working with clinician scientists here at HKU and worldwide to advance computing-powered imaging technologies and explore their clinical values in the coming years," said Professor Wu.
"Nuclear magnetic resonance is a gift from nature since nature endows us humans with a vast quantity of MRI-visible water molecules, and we must utilise this magnetic resonance physics phenomenon more for the benefit of humanity." He added.
Link to the Science paper: https://www.science.org/stoken/author-tokens/ST-1847/full
Link to Science Perspective article: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adp0670
Hashtag: #HKU
The issuer is solely responsible for the content of this announcement.







